… what is the level of scale in your water? Hard to say, I’d imagine. But, over time, believe me, you’ll know. Scale, also known as limescale, refers to mineral buildup—primarily magnesium and calcium—that creates a white, chalky-like substance that can accumulate on the plumbing system’s internal components, including water heaters, pipes, and fixtures, says Randall Oshiro, Lead Engineer, Noritz America.
In other words, “Common in household water, especially in areas with hard water, scale is essentially the crusty stuff you sometimes see on old pipes or the heating element of an old kettle,” says Ben Tate, National Sales Manager—Water Treatment, Navien, Inc. “When water is heated, these minerals crystallize and stick to surfaces such as the interiors of pipes, boilers, and heaters, forming a hard, insulating layer. It’s a natural process, but not exactly a welcome one, as it hampers the efficiency of any appliance it settles in.”
Scale’s Geography
Scale’s prevalence comes down to the geological makeup of the land through which your water travels. Water is a universal solvent, and as it moves through soil and rock, it picks up minerals like calcium and magnesium. In areas rich in limestone and other calcareous rocks, which are composed mainly of calcium carbonate, water tends to carry a higher load of these minerals. Consequently, regions with such geological features—think of areas like Texas and Florida—often struggle more with hard water and, by extension, scale.
Calcium and magnesium are naturally occurring minerals, says Oshiro. Depending on where the water is drawn from, water flowing through ground sources that contain high concentrations of these minerals will absorb some of the minerals. For example, water drawn from an aquifer with a high concentration of limestone will inevitably have a high concentration of lime (calcium). Like the previous example, areas where water is drawn from underground are often where the highest concentration of hard water exists.
A Water Heater’s Nemesis
Yet the “damage” scale can bring can’t be overstated, says Dan Giosia, Assistant Product Manager, Bradford White Corporation, “The accumulation of scale in a water heating system diminishes the overall performance, efficiency, and lifespan of the water heater unless preventative maintenance measures are implemented.”
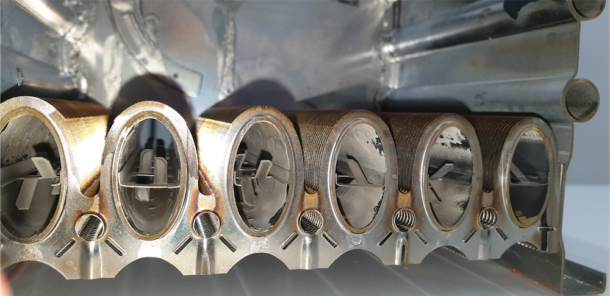

Scale poses a triple threat to water heating systems, says Tate. First, it’s an insulator. In a domain where efficient heat transfer is key, scale is a formidable barrier that keeps heat from doing its job effectively, which can drive up energy costs as your system struggles to keep up. Second, scale buildup increases the pressure in water lines and heating chambers, which can lead to leaks or mechanical failures. Lastly, the more energy and repairs a system requires, the more its lifespan diminishes. That’s why preventing scale isn’t just about maintaining water flow; it’s about saving money and extending the life of your equipment.
According to Oshiro, the primary danger of this scale formation is that it can accumulate inside the water heater (on the heat exchanger of tankless water heaters, along electrical heating elements, or along the internal flue of gas storage water heaters). This scale formation acts as an insulator in large amounts, preventing the proper heat exchange between the water and the heating source. “When this happens, the temperature will increase—as heat is not being drawn away at the designed rate—leading to increased thermal stress and decreased longevity of the internal components. Additionally, this buildup can reduce the surface area of piping, which can reduce the flow performance of the fixtures as well,” says Oshiro.
Tankless Magnified
Scale impacts both tank-type and tankless water heaters, though it manifests differently in each system, says Tate. In tank-type heaters, scale settles at the bottom of the tank, reducing heat transfer efficiency and leading to increased energy consumption and potential corrosion. Over time, this can significantly shorten the lifespan of the heater. Conversely, tankless models, which heat water directly, experience scale buildup directly on their heat exchangers. This can decrease heating efficiency and disrupt water flow, though it does not necessarily indicate a greater susceptibility to scale than tank-type heaters.
Regardless of the system type, the key to mitigating scale effects lies in regular maintenance. Both tank-type and tankless water heaters benefit from routine descaling and the proactive use of water treatment solutions like water softeners or scale inhibitors. Properly maintained, both systems can handle scale effectively, ensuring efficient operation and extending the lifespan of the heater. Thus, neither system is disadvantaged by scale when properly cared for, allowing users to choose based on their specific needs and preferences.
The reality is the mechanism/issue is about the same for both types of technology. “However, it will present itself much sooner/more apparently with a tankless type water heater than a tank-type water heater. The reason for this is basically that the pipes are smaller. Imagine a ¾” pipe and 24” round storage vessel. The smaller pipe, with a ¼” of scale buildup, loses significantly more of its surface area in comparison. This means that issues like reduced flow will become more apparent sooner,” says Oshiro.
However, it should be noted, continues Oshiro, that this same amount of scale will have the same actual effect on the systems (reduced efficiency, higher thermal stress). As a result, a tankless water heater may show signs of decreased performance sooner; however, this also allows the customer to preemptively conduct maintenance to ensure that the product will last many times longer than a storage tank-type water heater.
The storage tank-type water heater often continues to build up this scale over time, resulting in lower efficiencies (meaning higher operating costs) and eventual failure sooner. This scale formation is one of the primary mechanisms by which water heaters will fail. 1
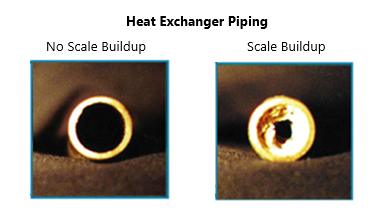
According to Bradford White’s Giosia, scale does pose a greater issue for tankless water heaters compared to tank-type water heaters due to their compact heat exchanger design. With a limited surface area and brief heating period, tankless heaters must rapidly elevate water temperatures, requiring high temperatures within the heat exchanger. As a result, scale tends to accumulate on this surface. If scale buildup becomes excessive, it can restrict water flow through the heat exchanger to the point of causing component or unit failure so it’s important for homeowners to contact their plumbing professional for regular maintenance.
In comparison to gas tank-type water heaters, electric tank-type heaters are generally more susceptible to scale buildup. This is primarily due to the very hot surfaces of electric heating elements, which have a small area and are prone to accumulating limescale within the tank. However, the impact of scale buildup is limited by the fact that electric heating elements are relatively inexpensive to replace, especially when compared to the cost of replacing a tankless gas heat exchanger or complete unit.
Gas tank-type water heaters may vary in susceptibility to scale buildup depending on their design. Units with a burner located outside the tank are typically less affected by scale compared to those with an internal heat exchanger where scale can accumulate.
Action Plan
What can contractors/homeowners do to “combat” scale? “The first step is to know your water supply,” says Oshiro. “Almost every municipal water supply company will annually publish a water quality report that will include data about the hardness of your water supply. This rating will often be rated on a scale of grains per gallon (gpg), parts per million (ppm), or milligrams per liter (mg/L). These ratings tell the density of mineral hardness (calcium) present in the water supply. The USGS[1] has a relative hardness indicator, where 61-120 mg/L (3.6-6 gpg) would be considered somewhat hard water.”
The best way to reduce scale is to treat the cause. This means using water treatment devices to prevent the calcium from building up in your water heater and piping. However, this isn’t always possible, so maintenance can be conducted by a descale flush: running a deliming agent (ex., vinegar or a specialized deliming agent) solution through piping the water heater to neutralize the calcium. As calcium is a basic material (pH >7), the acidic deliming agent will neutralize the calcium and remove buildup.
It’s also essential to adhere to the manufacturer’s recommendations for preventative maintenance, including specific procedures and frequency, for their product, advises Giosia.
Regular descaling of the water heater is often recommended to minimize scale buildup on the heat exchanger of a tankless water heater. The frequency of preventative maintenance typically depends on the characteristics of the water supply in your area, such as whether it is heating hard or soft water.
Installing a water softener can help reduce the hardness of the incoming water into both tankless and tank-type water heaters. However, it’s important to consult with a plumbing professional to ensure compatibility and to follow their recommendations.
Navien’s Tate says contractors and homeowners in these regions should adopt a proactive approach to water treatment. Installing a water softener is one effective strategy; it replaces hardness ions like calcium and magnesium with sodium or potassium, preventing them from forming scale. Additionally, I’d recommend considering scale prevention systems, which are designed to transform hardness minerals into harmless crystals that won’t stick to surfaces. Regular maintenance checks are also vital—they help ensure that any potential scale buildup is managed before it becomes a serious issue.
If you know that your water source is hard water, Oshiro suggests that you can take action to alleviate the risks.
- Develop a routine maintenance plan: This can be done by “descaling,” or flushing, your water heater regularly, depending on usage and quality. Asking your water heater manufacturer or installer for recommendations on frequency is a great first step.
- Treat the water: There are ways to eliminate (sequester or remove) hard-water minerals from the water source. These include items like water softeners, which use an ion-exchange process to physically remove free calcium from the water, or products that use a polyphosphate media to sequester the calcium to prevent it from coming out of the solution when heated.
Technology Tips
Is there newer technology that could make the equipment more scale-resistant? “Indeed,” says Tate. “One of the latest advancements in this area is Template Assisted Crystallization (TAC), which is a highly effective technology for preventing scale without the use of chemicals or salt. TAC systems work by transforming the calcium and magnesium minerals in hard water into stable, harmless crystal particles. These particles then flow through the system without sticking to surfaces, effectively preventing scale buildup. This technology is particularly useful for protecting high-efficiency tankless water heaters from scale, ensuring they operate at optimal efficiency while extending their lifespan.”
To some degree, says Oshiro, the selection of materials, design of the heat transfer surface, and the temperature in which the system operates, all have roles to play in controlling the amount of scale formation.
- Materials with less surface roughness provide less chance for scale particles to attach.
- Systems with lower temperature rises can also slightly reduce the formation rate of scale.
There is constant research into reducing the harmful effects of scale formation in water heating products, but at its core, it is a challenging situation to avoid entirely.
According to Giosia, some tankless water heater models incorporate technology aimed at enhancing scale resistance, such as scale reduction technology and replacement filtration cartridges. Moreover, water softeners can serve a similar purpose in mitigating scale buildup.
However, despite these advancements, maintenance remains essential for all tankless water heaters to prevent excessive scale accumulation. Regular upkeep is necessary to ensure optimal performance and longevity of the unit.
In conclusion, the timeline for significant damage can vary widely depending on the water’s hardness and the frequency of system maintenance. In regions with very hard water and minimal preventive measures, says Tate, significant scale buildup can occur within just a few months, leading to efficiency losses and potential system failures. Conversely, with proper management and regular maintenance, scale-related damage can often be staved off for years, preserving the efficiency and extending the life of the system.
1
https://www.usgs.gov/special-topics/water-science-school/science/hardness-water#:~:text=Measures%20of%20water%20hardness&text=General%20guidelines%20for%20classification%20of,mg%2FL%20as%20very%20hard



